汉诺塔及其React实现

28 Apr 2017
Author:wuguanxi
0、汉诺塔(hanoi)
汉诺塔(又称河内塔)问题是源于印度一个古老传说的益智玩具。大梵天创造世界的时候做了三根金刚石柱子,在一根柱子上从下往上按照大小顺序摞着64片黄金圆盘。大梵天命令婆罗门把圆盘从下面开始按大小顺序重新摆放在另一根柱子上。并且规定,在小圆盘上不能放大圆盘,在三根柱子之间一次只能移动一个圆盘。
=> 具体demo请戳 <=
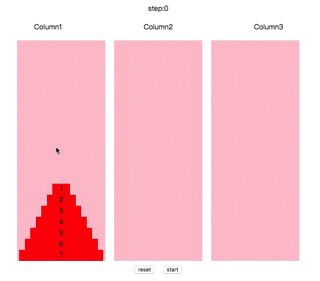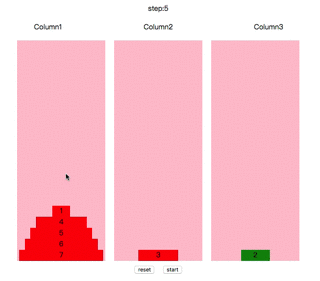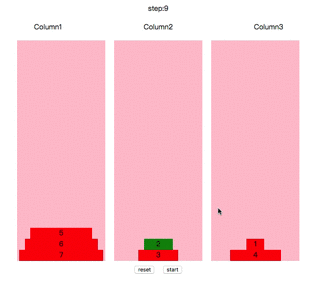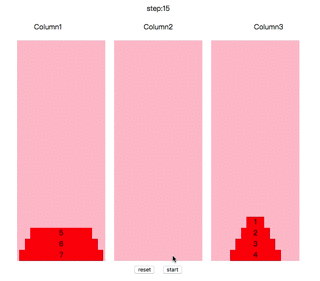
操作方法:鼠标点击任意柱子,会选中顶端的圆盘,再点击其他柱子,如果能符合规则,会自动移动到其上面。
=> github源码 <=
1、基于React的前端实现
a.组件
这个Hanoi我只拆成两个组件,分别是Hanoi.js 和 Column.js ,对应主体部分和柱子 其中Hanoi.js的render函数
// Hanoi.js
export default class Hanoi extends Component {
constructor(){
super();
this.state = {
columns:['Column1','Column2','Column3'],
lock:false,
step:0,
Column1:[/* { num : 1, color : 'red' } */],
Column2:[],
Column3:[],
st:'static', // static => catch => static
};
}
...
render (){
return (
<div className='container'>
<div className="step">step:{this.state.step}</div>
<div className="top">
<div className="name">Column1</div>
<div className="name">Column2</div>
<div className="name">Column3</div>
</div>
<div className='Hanoi'>
<Column list={this.state.Column1} clickFn={this.clickFn(0)} />
<Column list={this.state.Column2} clickFn={this.clickFn(1)} />
<Column list={this.state.Column3} clickFn={this.clickFn(2)} />
</div>
<button onClick={this.reset.bind(this)}>reset</button>
<button onClick={this.start.bind(this)}>start</button>
</div>
);
}
}
// Column.js
export default class Column extends Component {
constructor(){
super();
}
render (){
let { list , clickFn } = this.props;
let lis = list.map((item,index) => {
return <li key={index} style=>{item.num}</li>;
});
return (
<ul onClick={clickFn} className='Column'>
{lis}
</ul>
);
}
}
b.数据结构
数据结构非常简单,用3个js数组实现,用push进栈 pop方法出栈。
// hanoi的数据结构
this.state = {
...
Column1:[/* { num : 1, color : 'red' } // 圆盘的数据结构 */],
Column2:[],
Column3:[],
...
};
c.状态
整个Hanoi只有两种状态,分别是静止状态(static)和 选中状态(catch)选中状态时,被选中的圆盘会变色。
d.点击事件
点击柱子是,判断如果现在Hanoi是 静止状态(static)会选中该柱子最上的圆盘,同时Hanoi切换成 选中状态(catch), 然后其他柱子点击时,判断是在 选中状态(catch),如果点击的柱子符合规则能移动圆盘,圆盘移动并恢复颜色,同时Hanoi切换回 静止状态(static)。
// 事件的具体代码实现
click(name){
if ( this.state.st === 'static' ) {
if ( this.state[name].length > 0 ) {
this.state[name][this.state[name].length - 1].color = 'green';
this.state.st = 'catch';
this.setState({
[name]:this.state[name],
st:this.state.st
});
}
} else if ( this.state.st === 'catch' ) {
let catchItem = this.findCatch();
if ( this.state[name].length === 0 || this.state[name][this.state[name].length - 1].num >= catchItem.num ) {
[ this.state.Column1, this.state.Column2, this.state.Column3 ].forEach((item,index,array)=>{
if ( item.length > 0 && item[item.length - 1] === catchItem ){
array[index].pop();
}
});
catchItem.color = 'red';
this.state[name].push(catchItem);
this.setState({
Column1:this.state.Column1,
Column2:this.state.Column2,
Column3:this.state.Column3,
st:'static',
step:++this.state.step
});
}
}
}
自动排列

0. 每隔100ms执行一步
直接上代码
// 延时100ms执行click方法 返回 Promise
timeoutClick(name){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(()=>{
this.click(name);
return resolve();
},100);
});
}
1. 具体分析
hanoi玩多了,其实可以总结出 3部曲 比如现在我们的目标是:初始状态下将 num = 2 的圆盘 移动到 第二根柱子(Column2) 下面开始3部曲
-
- 将 num = 1 的圆盘移动到 除所在柱子( now = Column1 )和目标柱子( where = Column2 )的柱子(other = Column3 )
-
- 移动 num = 2 的圆盘到 目标柱子( where = Column2 )
-
- 移动 num = 1 的圆盘到 目标柱子 ( where = Column2 )
// 代码
move1toWhere(where){e
let origin = this.findNum(1);
return this.timeoutClick(origin).then(()=>this.timeoutClick(where)).catch((err)=>{console.log(err)});
}
move2toWhere(where){
let origin = this.findNum(2);
let other = this.findOther(origin,where);
return this.move1toWhere(other) // 第一步
.then(()=>this.timeoutClick(origin)) // 下面两行是第二步
.then(()=>this.timeoutClick(where))
.then(()=>this.move1toWhere(where)) // 第三步
.catch((err)=>{console.log(err)});
}
如果现在我们的目标是:初始状态下将 num = 3 的圆盘 移动到 第二根柱子(Column2)? 直接上代码
move3toWhere(where){
let origin = this.findNum(3);
let other = this.findOther(origin,where);
return this.move2toWhere(other)
.then(()=>this.timeoutClick(origin))
.then(()=>this.timeoutClick(where))
.then(()=>this.move2toWhere(where))
.catch((err)=>{console.log(err)});
}
聪明的同学们写到这里肯定已经发现规律了,没错就是递归 下面是递归正解
moveNtoWhere(n,where){
if ( n <= 1 ) return this.move1toWhere(where);
let origin = this.findNum(n);
let other = this.findOther(origin,where);
return this.moveNtoWhere(n-1,other)
.then(()=>this.timeoutClick(origin))
.then(()=>this.timeoutClick(where))
.then(()=>this.moveNtoWhere(n-1,where))
.catch((err)=>{console.log(err)});
}
借用一下知乎大神的说明:
一、把冰箱门打开; 二、把大象装进来; 三、把冰箱门关上
摘自万能的知乎 知乎的详细讨论